Programming often involves a lot of effort and expertise. But Low Code and No Code applications solve this problem. Because these platforms work with little or no coding at all. This can help small and medium-sized enterprises to meet the challenges of digitization. But how exactly do these development approaches work and what are the advantages and disadvantages? Here you will find everything you need to know about Low Code and No Code.
Low Code vs No Code Comparison - A Short Introduction
Usually, software is coded. However, this requires trained employees. For a few years now there has been a new possibility to have more complex applications created even by employees who are not software developers.
With the help of a user-friendly graphical user interface, such as a Drag-and-drop editor, it is possible for the developer to easily program applications.
The History of Low Code and No Code
The word Low Code first appeared in 2014 and can be translated as “minor code” or even “minor programming effort”. Particularly in the USA, the term has recently seen a true rebirth thanks to the development of so-called Low Code Development Platforms. These platforms should make it possible for users with little to no programming experience to construct applications since they allow the production of software or other applications with the least amount of coding possible.
It is a further development of the Rapid Application Development (RAD) approach. RAD was considered easy to learn, so even non-programmers could work with it easily.
KEY POINTS
- With Low Code and No Code, applications can be created easily.
- Little to no programming knowledge is required.
- It has evolved from the former Rapid Application Development.
How Does No Code work?
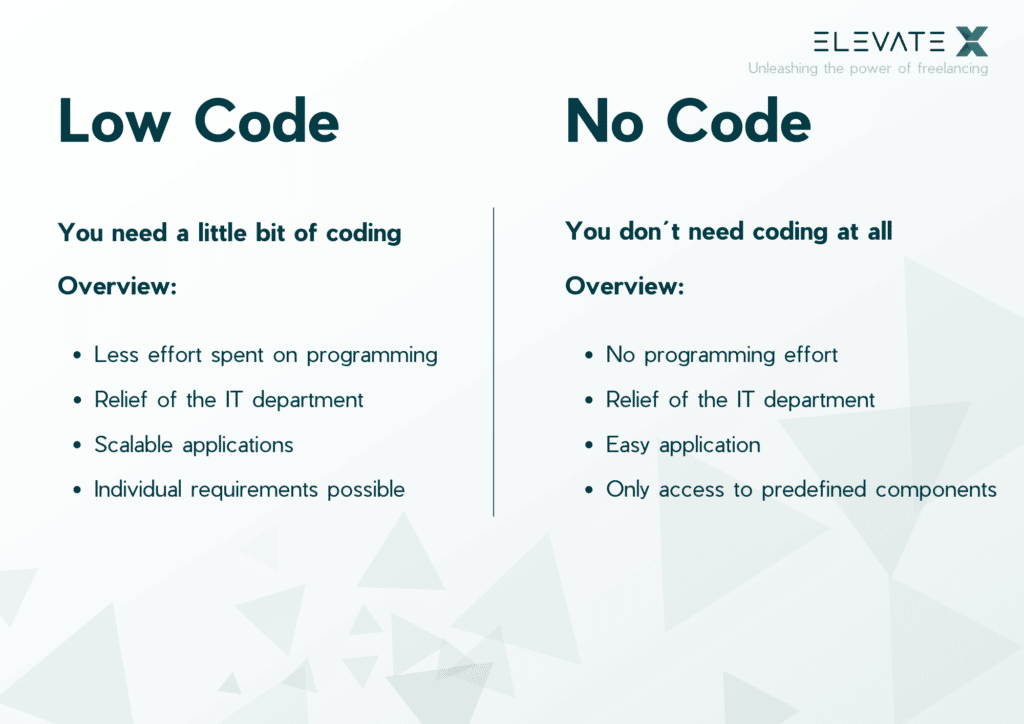
Apart from Low Code, there are also so-called No Code platforms, in which no programming at all is required. Platforms based on No Code not only not demand for further programming, but in some circumstances do not even enable it. Therefore, the majority of these services are primarily intended for untrained end users without programming experience, and in certain circumstances, even for private customers. For this purpose, specialized No Code platforms feature graphical user interfaces that enable the creation of applications based on the modular principle. Users can test and adjust their work progress again and again until the prototype meets their expectations.
The target audience for these platforms is lay developers, or non-IT professionals who operate in a variety of business tasks but lack programming expertise or proficiency yet still need to create applications.
How Does Low Code work?
Users of Low Code applications must, as the name suggests, know a little bit of coding. These platforms allow non-IT users to create applications for a variety of uses cases. Professional programmers and developers utilize Low Code platforms to provide applications to their business more quickly and to delegate routine programming duties to the platform so they may focus on more difficult and creative projects.
The WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) approach is a key tenet in the management of platforms like this. The development of graphical interfaces using visual editors is based on this idea. A graphical drawing area enhanced with certain structural components can be found on Low Code systems. Users can align these based on their own standards. The writing of the source code happens silently and automatically.
Low Code vs No Code Platforms: Pros and Cons
Pros
- Increased productivity: You can create more applications in less time. You can build applications in days or even hours because you don’t need to write many lines of code and have a lot of tools to automate tasks.
- Decreased costs: You can cut back on the expenditures associated with employing additional development tools and hiring more developers.
- Business agility: Low Code and No Code allow you to build frictionless applications that function on a variety of platforms and devices. Users may efficiently access and utilise data regardless of their location or the time of day.
- Effective Governance: Regulations regularly change, making it challenging for firms to stay current. You may stay risk-free by adhering to these requirements with the use of Low Code platforms.
Cons
- Running costs: There are often ongoing costs for this kind of platforms.
- Impossible to move to another systeme: Most platforms prevent downloading the code that was programmed in the background when the website was created, which makes it impossible to move to your own system.
- Individual user experience is not the focus: No Code Platforms are designed for particular use cases, where they boost operational process efficiency and productivity. Typically, user-defined extensions or integrations into other solutions are not supported by the makers.
- Waste of time: The usage of these technologies for activities that are excessively complex by lay developers or even professional development teams within organizations may lead to both the tool and the user becoming overwhelmed.
Need real code instead?
Find your seasoned Developer.
How to Use Low Code and No Code
No Code Tools are often used with proprietary, or manufacturer-specific, tools. This indicates that the functionality cannot be expanded, in addition to the fact that the capabilities are constrained. This is not a problem at the departmental level, but there may be compatibility problems when used enterprise-wide or even across multiple enterprises.
It runs the danger of having an infrastructure that is too rigid or monolithic on an architectural level. The majority of platforms and vendors demand that No Code tools be used in their own private cloud. As a result, there is no longer any chance for flexible use in a private cloud or on-premises building.
Platforms for Low Code programming are typically significantly simpler to incorporate into the company IT infrastructure than those for No Code programs. They can be more effectively coordinated with IT governance needs. This is helped by scalable architectural designs. The use cases for apps developed with low code are thus not constrained to particular corporate divisions.
The open APIs, in addition to the scalable structures, provide extensibility. Flexibility is provided via the use and reuse in diverse work situations. It is possible to deploy both on-premises and in the cloud.
Low Code platforms give developers access through their APIs to tools for application testing, quality assurance, and performance. They can also incorporate the productive methods seen in No Code technologies at the same time. Through visual techniques, this speeds up development.
In general, these platforms are good for:
- Customer experience applications
- Applications for mobile devices
- Modernization of legacy systems
- Realization of innovative technologies in digitization
Did you know? With Low Code and No Code you can also quickly build Minimum Viable Products to evaluate a potential product.
Low Code or No Code?
You will probably ask yourself which of the two platforms suits your company.
Several criteria must be taken into account:
- Type and scope of the applications
- Size of the company
- The specific project and the challenges involved
You should also ask yourself the following questions:
- What effects does the corresponding platform solution have on internal communication and collaboration?
- To what extent does the development solution affect business developers or departmental staff in application creation?
- Should the application creation be complementary or integrated?
Do We Even Need Normal Development?
Low Code and No Code software development uses a visual technique instead of the usual method of writing code in a programming language.
This strategy guarantees that programmers can create web-based and mobile applications of any complexity. Low Code also automates a significant portion of the software delivery process. The majority of the work that developers do may be concentrated on providing business value thanks to pre-built alternatives for continuous integration and deployment and 1-click environments.
Contrary to popular belief, Low Code was not developed to replace conventional software in digital projects. In fact, when coupled, Low Code and traditional development can produce a large amount of commercial value.
Many businesses can accelerate development and control expenses by combining these two development methodologies. For instance, Low Code can be used to create the majority of a system’s functionality before programming teams are added to create the system’s more intricate, bespoke features.
Since good old coding allows unmatched freedom and flexibility, No Code and Low Code should be seen as a bonus to normal development.
The Best Low Code and No Code Platforms
- Zoho Creator: You can build cross-platform apps that interface with your existing processes, ranging from simple call logs to rich and complex ERPs.
- Visual LANSA: Enables rapid development, deployment, and operation of applications.
- Mendix: You can design impactful apps with this platform for app development to deploy and succeed more quickly.
Wrap up
Low Code and No Code can be a useful complement to traditional programming. The development of software and process automation is now faster, less expensive, and open to all users thanks to technology. Software developers alone are no longer capable of handling the enormous volumes of software and automation. That’s why it makes sense as an entrepreneur to empower your employees outside of IT to take development into their own hands.
The visual interface environment of a Low Code/No Code development platform allows developers to drag and drop application components, connect them, and create a mobile or web application.
Special No Code/Low Code platforms allow non-experts to create applications with little or no coding. The code is created automatically in the background.
The fact that it is much easier than normal programming saves a lot of time. In addition, you save costs as a company, because you no longer have to hire so many developers. In addition, you can easily make changes and therefore quickly adapt to new developments.