Companies and institutions constantly need new ideas and solutions to problems. But it is not easy to create them. However, there are methods to make these tasks easier. When it comes to the well-being of humanity, Design Thinking is recommended. But what is it actually? You can find a detailed explanation of Design Thinking here.
What Is Design Thinking?
If you want to translate the term Design Thinking into German, the translations creative or constructive thinking would fit best. It is therefore a special form of thinking. As you will understand later in this guide, Design Thinkers deliberately follow a number of phases: We are talking about the so-called Design Thinking Process. Those who successfully apply the method are in many cases rewarded with innovative ideas. This is also the purpose of Design Thinking: In our modern world, mankind needs in different dimensions new ideas and high-quality solutions to problems. The approach thus promises to make it easier to achieve these ambitious goals. Moreover, the focus is always on people and their needs. Nevertheless, the economy and products also play a small role.
Where Is Design Thinking Used?
Design Thinking can be applied in many areas of society because almost everything is currently becoming more demanding due to the numerous unusual upheavals. We are confronted with problems such as digitalization, globalization, and climate change, and this list can be extended by countless other points. Everyone feels the enormous acceleration of life and the increasing complexity – in both private and professional contexts.
Nevertheless, it is mainly companies and institutions that apply Design Thinking in order to better compete on the market in the present and the future. Since the Design Thinking process, through its successive phases, provides a systematic approach to finding solutions for problems, it is easier to measure success. In addition, Design Thinking is primarily a method of teams. In many cases, these teams also work together on an interdisciplinary basis.
KEY POINTS
- Design Thinking stands for creative or constructive thinking that promotes the development of solutions to problems and innovative ideas.
- The Design Thinking Process according to the Hasso Plattner Institute (HPI) consists of six phases, the so-called iterative process.
- The phases are: Understanding, Observing, Defining Viewpoint or Point of View, Finding Ideas, Prototyping, and Testing.
- For the greatest success, interdisciplinary teams should work together, if possible in variable workspaces.
Where Does Design Thinking Come From?
Design Thinking was developed in the 1960s. Terry Winograd, Larry Leifer and David Kelley, who were each professors at the U.S. University of Stanfort, were responsible. At the time, they founded IDEO, a design and innovation agency that provides consulting services. The company applies the Design Thinking concept itself.
Later, German SAP founder Hasso Plattner also became aware of Design Thinking. After Winograd, Leifer and Kelley founded the d.school at Stanford University, Plattner got on board. The institution was eventually renamed the Hasso Plattner Institute of Design. In 2007, the HPI School of Design Thinking followed in Potsdam, Germany. Research projects on Design Thinking also take place here.
How Does Design Thinking Work?
Design Thinking is a method with which projects, innovations, portfolios, analyses as well as developments can be carried out or created. The thinking approach is particularly promising when three points come together:
- An interdisciplinary team
- A variable working environment
- The Design Thinking Process
Multi- or interdisciplinary teams allow you to step beyond the boundaries of a specialist field. This creates a good basis for the development of innovative ideas. In addition, complex issues can be handled more easily when know-how from different areas comes together. The teams consist of only few people, ideally five or six. Often, one representative per discipline is sufficient. The people should be selected on the basis of their emphatic abilities, because Design Thinking deliberately focuses on people.
Variable workspaces are recommended as a working environment for the interdisciplinary team. This means that the working environment can be used flexibly. To make this possible, the workspace should provide each member of the team with plenty of room to develop freely. In addition, a selection of tools for thought processes is helpful. These include for example, whiteboards. The choice of furniture should not be underestimated. It should at least be ergonomic. To encourage creativity, companies can also provide standing workstations and other innovative furniture.
In addition to interdisciplinary teams and a variable working environment, the development of innovative ideas and solutions for complex problems requires the six-phase Design Thinking process. You can learn more about the individual phases in the next section.
Need a project manager?
We have the right expert for you.
What Are the 6 Phases in Design Thinking?
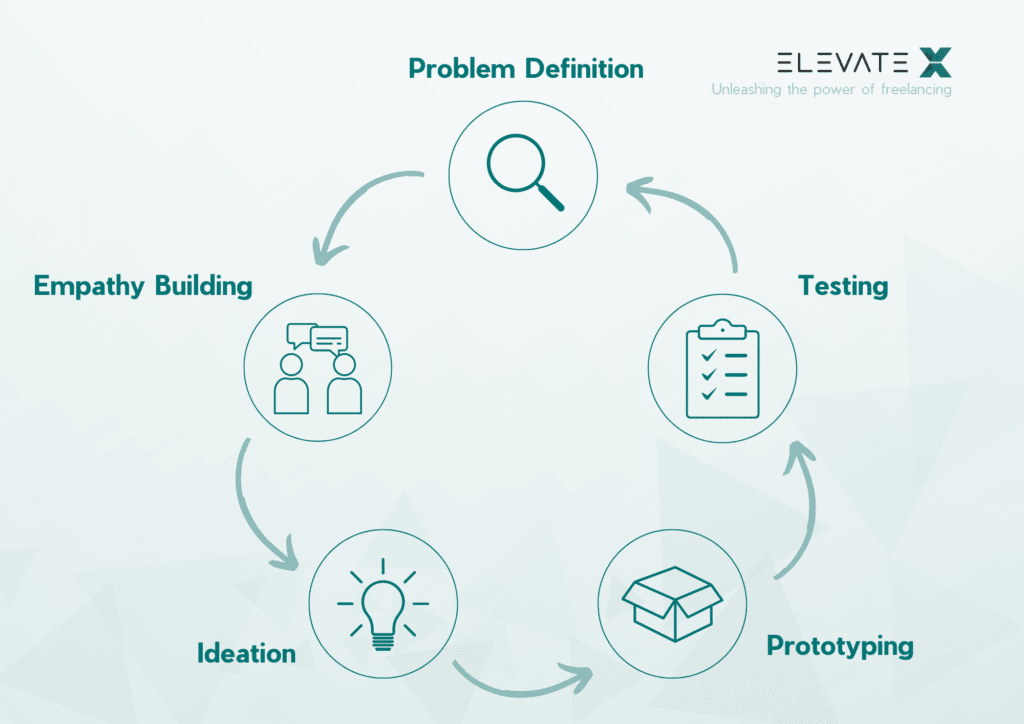
The Design Thinking Process consists of six phases. These are run through again as needed. This is then referred to as an iterative process or an iterative loop. When going through the individual phases, the focus is on people. This is one of the basic requirements in Design Thinking. In addition to this six-phase Design Thinking Process, which is designed according to the Hasso Plattner Institute in Potsdam, there are also some other models.
Phase 1: Understanding
First, the problem must be understood in the Design Thinking process. To start with, a research takes place. Then, each member of the multidisciplinary team can create and present his or her own definition. Nevertheless, the phase should end with a general definition that is shared by all team members. In addition, the development of the solution is already part of the considerations. The team can go through some W-questions for this, for example:
- What are the problems?
- What is the specific goal?
- For whom do we develop a solution?
- What could make their lives easier?
- What conditions must be considered?
Phase 2: Observe
The team will observe the customer in phase 2. Among other things, conversations and interviews can be used. Above all, it is about better understanding people and their needs and to examine the problem from all sides. The team should consist of good listeners. It can also team up with experts who can contribute valuable input.
Phase 3: Define View
In phase 3, the team merges the results from the first two phases. The goal is to define a comprehensive view of the target group. The results are summarized both in writing and pictorially. Among other things, the point-of-view technique can be used for this purpose.
Phase 4: Find Ideas
With a classic brainstorming, phase 4 is initiated. When searching and finding good ideas, the participants are allowed to give free rein to their creativity. Even crazy ideas that are unrealistic at first glance are allowed. They may be impractical, but they can encourage other ideas. The point is to collect as many ideas as possible and not to interrupt the thinking process with criticism. The team evaluates all ideas and then sorts them into a list according to priority. Decisions should be made on the basis of feasibility, efficiency and cost.
Phase 5: Develop Prototypes
Based on the results of the brainstorming, a prototype is now developed. This does not have to be perfect by any means. The understanding of the solutions can be improved in this way, and it is also easier to develop ideas further in this way.
Phase 6: Testing
In the final phase, the target group is given the opportunity to test the prototype. They are given the opportunity to provide feedback. If an idea turns out to be unusable, it can be discarded. So it’s also a matter of the team remaining as flexible as possible until the very end.
Who Uses Design Thinking?
The company SAP is also known as a Design Thinking user. Within Germany, several other famous users can be found: Volkswagen, Siemens and Deutsche Bahn, among others, rely on the on the process. International brands that also use the concept are Swisscom, Pinterest and Airbnb.
Why Design Thinking?
Because failure is allowed in the Design Thinking process, criticism only plays a role at a late stage, and well-chosen thinkers come together, the probability is high that creativity will blossom abundantly. Many high-quality products have already been created in this way. These include the market-leading platform Airbnb.
Wrap Up
Design Thinking is about creative thinking. In the end, companies get innovative solutions to real problems of their customers and new ideas that the world really needs. The Hasso Plattner Institute has identified six phases that are useful for successful collaboration: the Design Thinking Process. This is carried out in iterative loops. This means that individual, several or all phases are repeated as needed. The fact that this thinking approach works is demonstrated by highly successful projects such as Airbnb, as well as companies like Siemens.
Design Thinking is an innovative thought process that brings together an interdisciplinary team. The goal is to develop new products that really help people.
The Design Thinking Process according to the Hasso Plattner Institute consists of six phases or Design Thinking Process steps. These are, in order: Understanding, Observing, Synthesizing, Ideating, Prototyping, and Testing.
Design Thinking is mainly used in companies and institutions. Wherever new solutions or ideas are needed for the well-being of people, the thinking approach can provide good services.