Free Tool
Compare Employment Costs of Freelancers and Employees
When is it worth hiring a freelancer and when is it worth hiring an employee? In today’s world of work, there are different employment models and the decision between hiring an employee and hiring a freelancer depends on many factors, including cost.
Freelancer vs Employee Cost Compared
- Freelancers are often the more economical choice for short-term (6-24 months) projects.
- Freelancers give companies a high degree of flexibility to deploy specialized skills as needed.
- In areas with long staffing times for employees, such as IT, freelancers offer an efficient, timely solution.
Freelancer And Employee Compared
Pros and Cons Freelancer
Pros
- Bring extremely specialized expertise from outside into the company.
- Possibility of knowledge transfer and training of own employees.
- No long-term costs such as salaries, insurance or social benefits.
- Ideal for short-term projects (6-24 months) or special skills that are not required on a permanent basis.
- Costs are directly attributable to the assignment.
- Freelancer motivation through the prospect of new projects and higher fees.
Cons
- Hourly rates can vary (greatly) depending on the freelancer.
- Unpredictable expenses, depending on project availability.
- Possible lack of continuity and integration into company culture.
- Uncertainty regarding long-term source of income.
Possible lack of corporate culture identification.
Pros and Cons Employee
Pros
- Predictable monthly expenses for the company through fixed salaries and additional benefits such as health insurance, pension plans and vacation.
- Suitable for long-term projects and continuous work assignments.
- Offer stability and the opportunity to integrate into the company culture.
- Motivated by career development and long-term prospects.
- Long-term commitment to the company.
Cons
- Total costs may be higher in the long term.
Less financial flexibility for the employer. - Costs are often not directly traceable to work performed.
- Less flexibility with changing requirements.
- Possible limitation of income to fixed salary.
- Possible lack of expertise and difficulty in filling specialized positions.
Cost Comparison Freelancer And Employee
- Long-term projects or continuous work: For long-term projects or a continuous workload, it may be more cost-effective to hire an employee. The fixed monthly costs for an employee may be lower than the variable costs for a freelancer over a longer period of time.
- Fluctuation and project demand: If the workload fluctuates greatly or projects are sporadic, hiring freelancers flexibly could be more cost-effective. Here, the company only pays for the work actually performed, without making long-term commitments.
- Additional costs for employees: Companies incur additional costs such as sick pay, vacation pay, benefits and possibly training for employees. These costs must be taken into account when calculating total expenses.
- Administrative overhead: Managing an employee involves administrative overhead that may be less when hiring a freelancer.
Practical Example: Freelancer vs. Employee
We often hear that employees are much more cost-effective than freelancers. This statement may seem correct at first glance when looking at the exact hourly wage. However, let’s take a closer look at the concrete numbers.
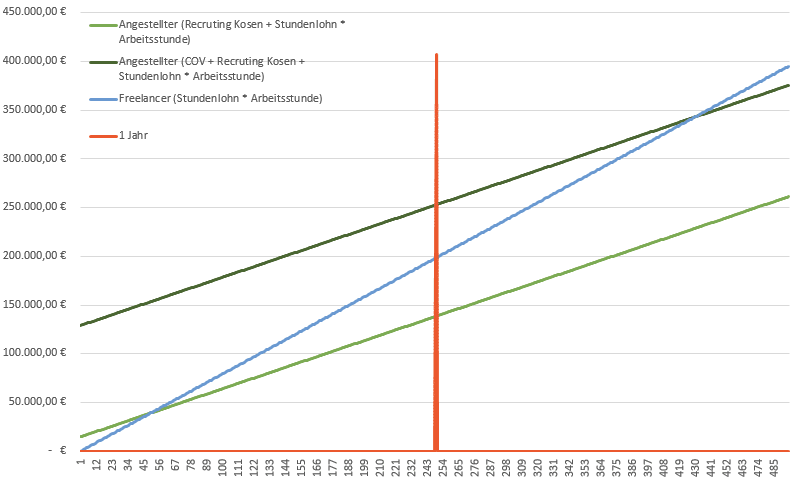
Consider an experienced backend developer as an example. As a freelancer, they might charge around 100 euros per hour. In permanent employment, we assume an annual gross salary of approximately 72,000 euros. However, as an employer, additional costs such as labor costs, work materials, training costs, and other expenses come into play.
Taking all these factors into account, the actual costs for the employee amount to about 96,307 euros per year. To calculate the hourly rate, we need to consider the available working time, after deducting holidays, sickness, training, etc. With a standard working time of 193 days per year, this results in an hourly rate of 62.38 euros. At first glance, the employee seems to be about 38 euros cheaper than the freelancer.
A crucial factor not to be neglected is the recruiting costs. Recruiting an employee requires resources and costs about 14,600 euros before productivity begins. This leads to the break-even point, where an employee becomes cheaper than a freelancer, at 48.7 project days. For short-term projects, collaboration with freelancers is therefore more economical. In this context, we usually speak of short-term projects when the project duration does not exceed two years.
In the IT industry, filling positions can be challenging, and it takes an average of 197 days to fill an IT position. In such cases, it may be sensible to hire a freelancer as a temporary solution until the right employee is found. Depending on the costs of the vacant position, long-term collaboration with a freelancer could even be cost-effective over 21.4 project months. This illustrates that, in certain situations, collaboration with a freelancer can be meaningful in the long run.
How much do freelancers really cost compared to employees?
Freelancer-Rates: You Pay for What You Get
A fundamental difference between a freelance developer and a permanent employee is that the client only pays the freelancer for the hours actually worked. If the freelancer is sick or on vacation, they do not receive any payment. In contrast, a permanent employee receives a fixed salary, regardless of whether they are currently working or not. If, for example, 28 vacation days and 15 sick days are assumed, this results in 43 days or 344 hours in which the employee is paid without working.
Freelancers, on the other hand, are only paid for the hours they actually work productively. As they are generally not on site and not involved in company processes, there are far fewer distractions for them. They can therefore focus entirely on their tasks.
The Impact of Unfilled Positions
Not filling a position can have negative effects in various ways and incur significant costs. The “Cost of Vacancy” refers to the direct and indirect costs that arise when a position remains unfilled for an extended period. Firstly, an unfilled position often leads to an overload of the existing team. Employees must take on additional responsibilities to fill the gap, leading to stress, overwork, and a decline in morale. This, in turn, can affect the team’s productivity and efficiency.
Furthermore, not filling a position can result in a standstill or delay in projects. Unfilled positions often mean a lack of specific skills or expertise crucial for progress. This can hinder the development of new ideas, products, or services and ultimately lead to revenue losses.
The Cost of Vacancy also includes direct financial impacts such as the costs of re-recruiting, training new employees, and potential revenue losses due to business disruptions. Additionally, customers may become dissatisfied due to lower service quality or longer waiting times, negatively impacting the company’s trust in the long term. Overall, not filling a position can have significant impacts on company performance and success, extending beyond purely financial aspects. In this case, using freelancers can be a meaningful strategy to mitigate the negative effects of an unfilled position. Freelancers offer a flexible solution to bridge gaps and distribute workload without undergoing lengthy recruitment processes. Their expertise and specialized skills enable them to effectively handle specific projects or tasks that would otherwise remain idle due to lack of resources or knowledge.
Although employing freelancers may incur costs, the short-term expenses are often lower than the longer-term costs of an unfilled position. This flexibility allows companies to bridge gaps, advance projects, and minimize the negative impacts of vacancy, while still having the opportunity to search for a suitable permanent employee in the long run.
