Free Tool
Cost of Vacancy – Calculator
Unfilled job positions can be costly for businesses, but many are unaware of this. By calculating the Cost of Vacancy, the importance of having an effective recruitment strategy and its impact on the company’s performance can be clarified. When senior management comprehends the potential loss of tens of thousands of euros each month due to vacant positions, they will likely prioritize including recruiters in the strategic decision-making process.
Cost of Vacancy - Key Points
- Cost of Vacancy describes the costs that an unfilled position causes in a company
-
The cost can be calculated with a simple formula:
Annual Salary / ⌀ Days Worked per Year x Factor x ⌀ Time to Fill
- An unfilled position can have many consequences, such as employee dissatisfaction, loss of productivity and customer dissatisfaction
What Does "Cost of Vacancy" Mean?
The Cost of Vacancy is a key figure for a company’s recruitment and is typically used to plan the recruitment budget. It reflects the costs incurred by a vacant position in a company. The ratio of this cost is based on the assumption that each employee contributes numerically to the company’s revenue, which means that an unfilled position represents a loss for the company.
Why Does a Vacant Position Cost the Company Money?
The costs of unfilled jobs are complex and may not be immediately evident. They are hidden costs that arise from various factors.
Individual Costs
On average, a manager should earn their company three to five times their annual salary. For instance, let’s consider an R&D manager who makes 120,000 euros annually. If this position is eliminated and left unfilled, the company could lose between 1,400 to 2,300 euros in daily revenue. If this role remains unoccupied for half a year, the expenses increase to roughly 300,000 Euro – an impressive amount, yet only a small percentage of the total impact an unfilled position can have on a company’s profits.
Real Costs
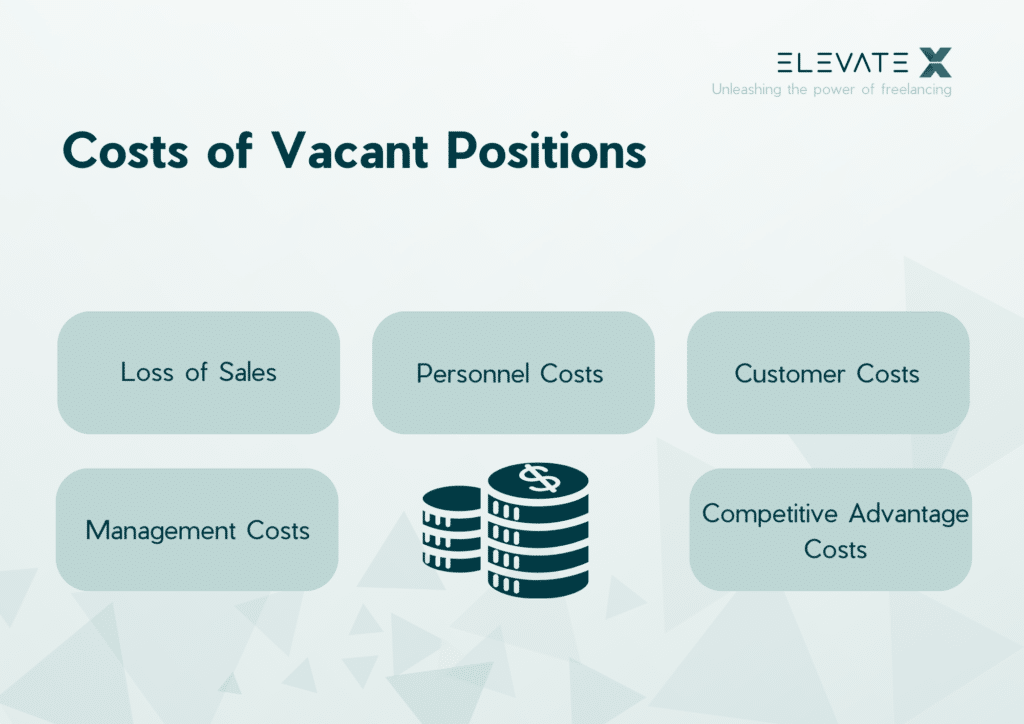
Loss of Revenue
- Delayed revenue resulting from increased Time-To-Market for new products
- Lost revenue due to products or services that could never be introduced
- Decreased output due to employees having to perform unfamiliar jobs
Personnel Costs
- Additional workload and higher stress levels
- More frequent occurrence of illness, absenteeism and unpunctuality
- Inability to focus on the development of existing employees
- Increased Frustration
- Higher scrap and rework/error rates
- Reduced opportunities for employees to achieve their individual goals
- Higher Fluctuation
- Less creativity and innovative thinking
Management Costs
- Additional workload for managers responsible for departments with vacancies
- Less time for the management of remaining employees
- Increasing frustration due to lack of support from the company
- Higher turnover in middle management (and often in senior management as well)
- Increased opportunity costs, as managers must spend valuable time on substitute tasks
Customer Dissatisfaction
- Loss of revenue due to delayed order fulfillment and service quality
- Increased customer turnover due to delays in the development and introduction of new products
- Image loss due to perceived process instability and declining service quality
Impairment of Competitiveness
- Company gives the impression of being vulnerable and unstable to the public
- The company’s reputation as an employer is negatively impacted and it sends a signal to potential employees that the organisation is experiencing difficulties
- Unfilled positions can lead to underutilization of resources
- Weakened corporate culture
All these factors culminate, initiating a downward spiral that may result in not only dissatisfied employees but also in lost revenue.
How to Calculate the Cost of Vacancy?
The cost of a vacant position can be calculated and depends on several factors:
- Gross annual salary of the position
- Working days per year (Holiday and sick days are not taken into account)
- Importance of the position as multiplication factor x. From 1 (necessary but less important), 2 (important) or 3 (essential)
- Time to Hire/ Time to Fill
This results in the following formula for calculating vacancy costs:
Annual Salary / ⌀ Working days per year x Factor x ⌀ Time to Fill
A Brief Example
Suppose a company has an open position for a software developer. The annual salary for this position is €62,000. The company assumes that there is an average of 250 working days per year. The multiplication factor is set to 2. The average time to fill the position is 120 days.
Annual Salary / ⌀ Working days per year x Factor x ⌀ Time to Fill
62,000€ / 250 x 2 x 120 = 59,520€
These figures result in a cost of vacancy of 59,520 euros. After just 4 months, the cost of a vacant software developer is therefore only slightly less than his annual salary. After one year, the cost of the unfilled position would already amount to 181,040 euros – almost three times the annual salary of this position. Accordingly, positions with a high influence factor in particular should remain unfilled for as short a time as possible.
What Is the Impact of an Unfilled Position?
Costs of vacancies may indeed adversely affect a company’s financial status. However, additional performance factors also play an important role.
Increased Team Workload
If an employee leaves their job, colleagues often have to take on their tasks until a replacement is found. This can result in a substantial increase in workload. Without any prospect of improvement, employee motivation declines, and dissatisfaction arises which, in the worst-case scenario, can lead to termination.
Slower Processes
If employees have to take on additional tasks, this slows down regular processes. Ambiguity in the allocation of work and the same amount of work with fewer personnel results in decreased productivity for a team.
Lack of Innovation
Overworked employees hardly have time for innovative and creative ideas. This slows down growth and affects the company’s competitiveness in the long term.
We’ll help you fill your vacancies!
What Is the Best Way to Fill a Vacant Position?
In times of skill shortages and the ‘war for talent’, where companies struggle to fill their vacancies with suitable candidates, it is essential to proceed strategically to establish oneself as an attractive employer. This is especially important when vacancies arise unexpectedly, as speed is crucial for the reasons mentioned above and recruiting becomes a critical process for success. There are several ways to fill an unfilled position.
Flexible Resource Management
These include models that enable companies to respond flexibly to their staffing needs. In particular, freelancers provide a perfect solution for efficiently bridging short-term bottlenecks.
Active Sourcing
One way to reduce the duration required to fill a job position is to actively search for candidates yourself. In active sourcing, companies specifically search for suitable candidates and contact them. Although this can be time-consuming, it shortens the time it takes to fill a position.
Outsourcing
Another type of sourcing that involves actively outsourcing certain tasks to external, specialized freelancers or contractors.
Talent Pools
Establishing a talent pool to keep in touch with previous, skilled applicants increases the chances of being able to hire suitable candidates more quickly in the future. Another option is to utilize existing personnel databases from a personnel service provider or consider employee leasing.
Workforce Management
Through efficient resource planning and strategic task allocation as part of workforce management, existing employees can temporarily take on additional responsibilities to bridge the bottleneck. This gives the company time to find a suitable solution without productivity and quality of work suffering. This allows greater flexibility to respond quickly to staff shortages and helps bridging vacancies.
Conclusion
The costs of an unfilled position are not explicitly listed on your company’s financial statements, but they do exist and can have a significant negative impact. Alongside a decrease in efficiency and productivity, employee discontent also plays a major role. Consequently, it is recommended to be aware of these expenses and fill positions as quickly as possible in order to minimize possible negative effects.
Cost of Vacancy describes the costs that an unfilled position causes in a company.
Annual Salary / ⌀ Working days per year x Factor x ⌀ Time to Fill
Vacancy costs stem from the interplay of various factors. Loss of revenue due to reduced productivity and service quality, employee dissatisfaction due to increased workload, and restrictions on growth due to a lack of time for innovative and creative thinking represent only a handful of potential causes of vacancy costs.
