In today’s fast-paced technology world, efficient and flexible project management methods are essential. Agile methods, particularly Scrum and Kanban, have proven to be extremely effective in managing projects dynamically and effectively. Kanban vs Scrum, which method is suitable for which project? In this article, we explore these two popular methods, their workings, benefits, and when they are best applied.
What is Agile Project Management?
Agile project management is an approach characterized by flexibility, customer focus, and rapid adaptation to change. Agile project management is a dynamic way of working that occurs in short cyclic stages, known as sprints. Instead of following rigid, long-term plans, it focuses on flexibly adjustable, clearly defined project segments.
This method allows teams to quickly respond to changes and continuously introduce improvements. By focusing on teamwork and customer engagement, a direct, reactive working style is encouraged. Agile project management is ideal for projects where flexibility and rapid adaptation to new conditions are essential – in line with the word “agile,” which means agility and adaptability, ideally reducing project risks.
This approach is particularly popular in industries like IT and software development, where requirements can change rapidly. Kanban and Scrum are the most popular methods of agile management.
KEY POINTS
- Agile project management is characterized by flexibility and rapid adaptability, making it ideal for dynamic projects.
- Kanban vs Scrum: Scrum is suitable for structured projects with fixed goals, based on regular sprints and defined roles, and also promotes continuous improvement.
- Kanban vs Scrum: Kanban is appropriate for continuous, flexible workflows, utilizes visual workflows, and limits tasks being worked on simultaneously to increase efficiency.
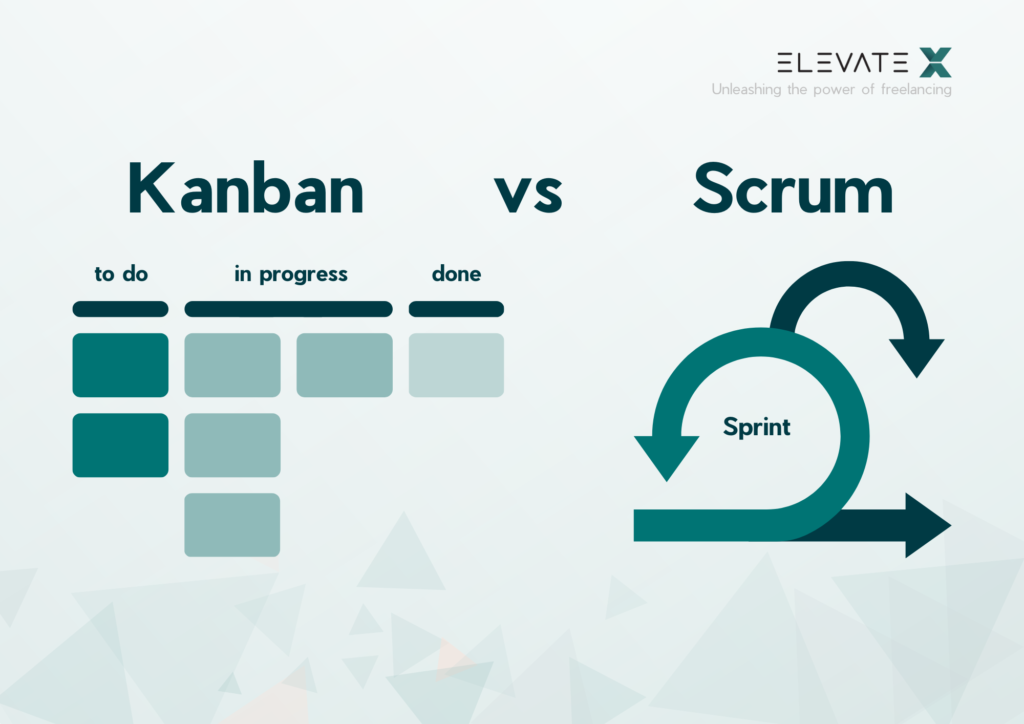
Kanban vs Scrum
Although both methods are agile, they have different approaches and structures. Scrum is more structured with its defined roles and timeframes, while Kanban offers greater flexibility in terms of workflows and prioritizations.
Kanban vs Scrum: What Do the Methods Have in Common?
Despite their differences, Scrum and Kanban share some fundamental similarities that make them popular agile methods:
Agile Principles
Both methods are based on the principles of agile management, such as flexibility, adaptability, and a focus on continuous improvement.
Customer Orientation
Both Scrum and Kanban place great emphasis on maximizing customer value and adapting to customer needs.
Transparency and Visualization
Both approaches promote transparency and a clear representation of the work process, which contributes to improved communication and coordination within the team.
Flexibility in Prioritization
Kanban and Scrum allow for flexible prioritization of tasks, enabling teams to quickly adapt to changing requirements.
Kanban vs Scrum: What are the Key Differences?
Despite these similarities, Scrum and Kanban differ in several key areas:
Time Frames
Scrum works with defined sprints, where tasks must be completed within a specific time frame. In contrast, Kanban does not have a set time frame for task completion, allowing for a continuous workflow.
Roles and Responsibilities
Scrum has defined roles such as the Product Owner and the Scrum Master. Kanban, on the other hand, relies on a less structured team setup without defined roles, promoting a flatter hierarchy.
Delegation and Prioritization
In Scrum, tasks are prioritized and assigned at the start of the sprint, while Kanban allows for ongoing prioritization and assignment of tasks.
Handling Changes
In Scrum, changes are usually made between sprints, while Kanban enables teams to make changes at any time.
Metrics
Scrum uses metrics like Sprint Burndown Charts for performance measurement, whereas Kanban uses throughput times and the number of completed tasks as metrics.
The choice between Scrum and Kanban should be based on the specific needs of the project, the team structure, and the working environment. Both methods offer different advantages that can be ideal in various situations and for different team dynamics.
Looking for a Project Manager?
Kanban Method
The Kanban method is an approach in agile project management focused on efficient workflows and continuous improvement. Originating from lean production, Kanban utilizes visual aids, typically a Kanban board, to track and manage work progress. Tasks are categorized on the board into sections like “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” This allows teams to transparently track progress and quickly identify bottlenecks.
Kanban emphasizes limiting ongoing work to prevent overload and ensure even work distribution while allowing flexibility and continuous improvement of work processes. It is a versatile method that can be applied in various industries and projects to enhance efficiency and team collaboration.
Originally developed by Toyota in 1947, Kanban has also proven effective in IT and software development.
How Does Kanban Work?
Kanban is based on a visual system that represents tasks and their progress on a Kanban board.
Visualization of the Workflow
Tasks are represented as cards on the Kanban board and move through different stages of the workflow, such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” “In Review,” “Blocked,” and “Done.” This visualization allows teams to monitor progress and identify bottlenecks.
Limitation of Work-in-Progress (WIP)
To prevent overload and increase efficiency, the number of tasks being worked on simultaneously is limited. This promotes consistent workload and improves responsiveness to changes.
Adaptability and Continuous Improvement
Kanban teams continuously adapt their work to respond to changing priorities or new requirements. This flexibility allows for immediate attention to urgent matters.
Roles in the Kanban Team
Unlike Scrum, which has specific roles like Scrum Master, Kanban does not have defined roles. The entire team is responsible for the Kanban board, and some teams appoint an Agile Coach for support.
Metrics and Analysis
Key metrics in Kanban include lead and cycle times. Teams aim to improve their cycle times, supported by tools like the Cumulative Flow Diagram. This diagram helps measure the number of tasks in each phase and identify bottlenecks.
Kanban thus promotes a dynamic and agile way of working, characterized by high self-motivation in the team and strong cohesion. It is particularly suitable for teams facing many requests of varying priority and size and preferring a continuous workflow.
What are the Advantages of Kanban?
Kanban offers several benefits, making it an effective method for many teams and projects:
- Visualization of the Workflow: The Kanban board provides a clear visualization of all tasks and their status. This promotes transparency and facilitates the identification of process bottlenecks.
- Flexibility: Kanban allows high adaptability to changing priorities and requirements without disrupting the overall project flow. Teams can quickly respond to changes.
- Continuous Improvement: Through constant monitoring and adjusting of the workflow, teams can continuously improve their processes. Kanban encourages the principle of ongoing optimization.
- Limitation of Work in Progress: Limiting the number of tasks being worked on simultaneously prevents overload and increases efficiency.
These advantages make Kanban an ideal tool for teams seeking a flexible, transparent, and efficient method to manage their work processes.
Scrum Method
Scrum is an agile methodology originally developed for software development teams, but today it is also used in other industries. It is characterized by a structured approach focused on continuous improvement and iteration.
The core of Scrum is an incremental, iterative process: various product versions are created in individual, self-contained phases (= sprints), which are repeated until a satisfactory, final product is achieved. Scrum teams commit to delivering useful work increments at the end of a sprint period. This approach is based on the principle of learning from customers and improved decision-making through small work progress.
How Does Scrum Work?
Sprint Rhythm
Scrum projects are divided into sprints of two to a maximum of four weeks, each with fixed start and end dates. These time windows require complex tasks to be broken down into smaller stories to achieve quick learning effects.
Sprint Elements
- Daily Scrum: Daily stand-up meetings for coordination and problem-solving.
- Sprint Review: Evaluation of the work at the end of each sprint.
- Sprint Retrospective: Reflection and discussion for continuous improvement.
Scrum Roles
- Product Owner: Represents customer interests, manages the product backlog, and prioritizes tasks.
- Scrum Master: Supports the team in adhering to Scrum principles.
- Development Team: Determines the tasks to be completed, delivers interim results, and collectively takes responsibility for achieving goals. Scrum teams are self-organized, without internal hierarchy.
Scrum Metrics
These data points help teams improve efficiency and effectiveness. For example, metrics such as sprint goals, team velocity, and team capacity can be used during the sprint planning phase. These metrics can also measure progress towards sprint goals during daily stand-ups.
Change Philosophy
While Scrum teams commit to delivering the desired results at the end of the sprint, they also respond to customer feedback and adjust sprints accordingly to increase customer value. During the sprint retrospective, teams discuss how they can minimize changes in the future to avoid jeopardizing the delivery of interim results.
Scrum is therefore an empirical approach based on trial and error. Teams develop working solutions in the sprints, test them, and use the insights gained for the next step. Regular planning and daily stand-up meetings, where progress and obstacles are discussed, are important in this process.
What are the Advantages of Scrum?
Scrum, as a structured agile framework, offers various advantages that make it particularly suitable for certain projects and teams:
- Structure and Clarity: Scrum provides clearly defined roles, responsibilities, and processes. This structure helps teams focus on tasks and work more efficiently.
- Continuous Improvement: Through regular sprint retrospectives and constant customer feedback, the team can continually improve and adapt its working methods.
- Focused Work in Sprints: Dividing work into sprints allows teams to focus on specific tasks, increasing efficiency and product quality.
- Rapid Responsiveness to Changes: Although Scrum is a structured method, it allows teams to respond flexibly to changes and maximize customer value.
- Transparency and Communication: Daily stand-ups and regular meetings promote transparency and communication within the team, contributing to problem-solving.
- Stronger Team Dynamics: Regular communication and collaboration within the team enhance team dynamics.
Kanban vs Scrum: Which Method to Choose?
The choice between Scrum and Kanban depends on the specific conditions and requirements of a project:
Scrum is suitable for: Projects that need clear goals and defined delivery dates, and where the scope of the project remains relatively stable. Scrum is ideal for teams that benefit from a structured approach with fixed roles and regular sprints.
Kanban is suitable for: Teams that require flexibility in terms of priorities and requirements, and whose work cannot necessarily be divided into fixed time phases. Kanban is particularly advantageous in environments where tasks are continuously incoming and outgoing.
The decision should be based on the characteristics of the project, the team dynamics, and the team’s working method. Both methods offer different strengths and can be adapted depending on the situation and the team’s needs.
Conclusion
The choice between Scrum and Kanban depends on the specific needs of your project and team. Both methods offer unique advantages and can be used in various situations to increase efficiency and productivity.
Agile project management is a flexible approach that emphasizes rapid adaptability and continuous improvement.
Scrum works with fixed sprints and roles, while Kanban offers a continuous workflow without fixed roles and timeframes.
Choose Scrum for structured projects with clear goals and Kanban for flexible, continuous tasks, based on your project requirements and team dynamics.