In this article, we will delve into the world of IT infrastructure and explore the advantages and disadvantages of two prominent options: Cloud and On-Premise. Whether you are an IT decision-maker or a freelancer, understanding these choices is crucial for making informed decisions.
What Is On-Premise?
On-Premise, often referred to as “on-prem,” is an IT infrastructure model where an organization hosts its servers, applications, and data within its physical premises, such as a data center or server room. In this model, all hardware, software, and networking components are owned, managed, and maintained directly by the organization itself. Let’s take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of On-Premise solutions:
Advantages Of On-Premise:
- Complete Control: One of the most significant advantages of On-Premise solutions is the level of control they offer. Organizations have the autonomy to configure and customize their infrastructure according to their specific needs and security requirements. This control extends to hardware specifications, software configurations, and network setups.
- Data Security: With On-Premise solutions, sensitive data remains within the organization’s physical premises. This setup reduces the risk of unauthorized access since data is not stored in external data centers or cloud environments. For businesses with strict data security and compliance requirements, this can be a crucial advantage.
- Compliance: Some industries, such as healthcare and finance, have stringent regulatory requirements that mandate the storage and management of data on-premises. On-Premise solutions provide the necessary control and compliance adherence for organizations operating in such sectors.
Disadvantages Of On-Premise:
- High Initial Costs: Setting up and maintaining an On-Premise infrastructure can be a substantial financial investment. Organizations need to budget for hardware procurement, software licenses, networking equipment, and skilled personnel to manage the infrastructure effectively. This upfront cost can be a barrier for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Limited Scalability: Expanding an On-Premise infrastructure can be a complex and expensive endeavor. Organizations must anticipate future growth accurately and invest in additional hardware and resources accordingly. Scaling up quickly to meet unexpected demands can be challenging.
- Maintenance Overhead: On-Premise solutions require ongoing maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting. This can be time-consuming and may necessitate a dedicated IT team to ensure the infrastructure operates smoothly. Frequent software patches, hardware upgrades, and security updates are all responsibilities of the organization.
KEY POINTS
- Cloud solutions offer flexibility and cost-efficiency, making them a preferred choice for many businesses.
- Assess your data security requirements carefully and consider the sensitivity of your data when choosing between Cloud and On-Premise.
- Regardless of your choice, ensure robust backup and recovery processes to safeguard your data.
What Is The Cloud?
The cloud, short for “cloud computing,” is a technology paradigm that has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals access and manage IT resources. Unlike traditional On-Premise solutions, where everything is hosted locally, cloud computing leverages remote data centers and networks to deliver various computing services over the internet. Here’s a deeper dive into the concept of the cloud, including its key advantages and disadvantages:
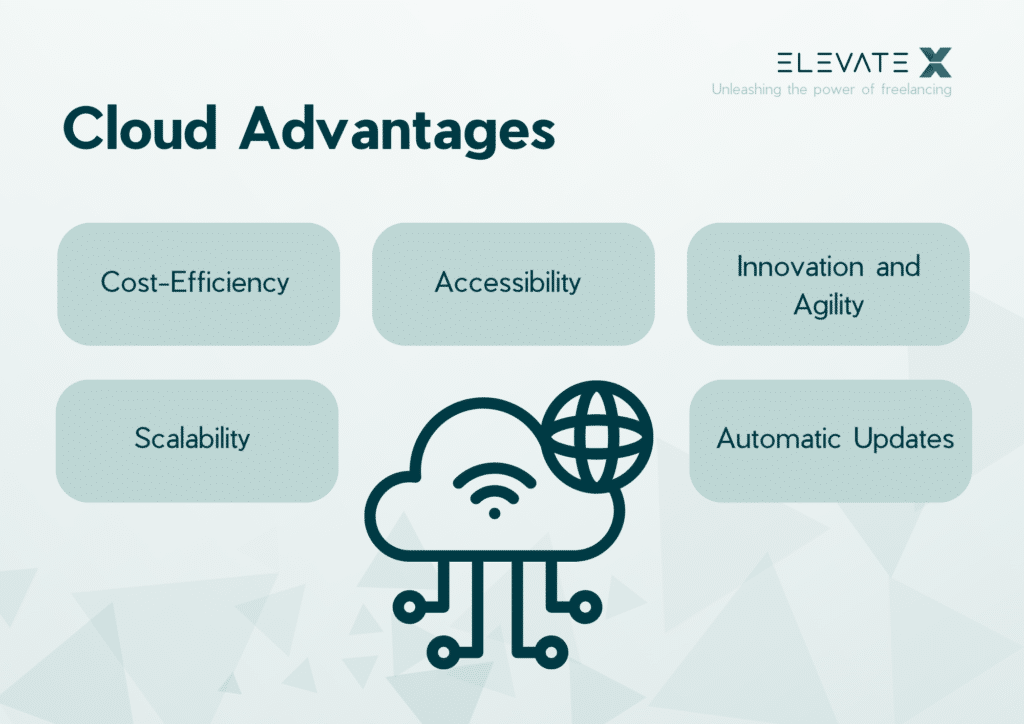
Advantages Of The Cloud:
- Cost-Efficiency: Cloud services often follow a pay-as-you-go or subscription-based model. This means organizations pay only for the resources and services they consume, reducing the need for large upfront investments in hardware and software. It’s a cost-effective approach, particularly for startups and businesses with fluctuating computing needs.
- Scalability: One of the standout features of the cloud is its scalability. Businesses can easily scale up or down their IT resources to accommodate changing demands. Whether it’s adding more storage, processing power, or software licenses, cloud providers offer the flexibility to adjust resources in real-time.
- Accessibility: Cloud services can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility promotes remote work and allows employees to collaborate seamlessly, irrespective of their physical location. It’s especially valuable in today’s globalized and mobile workforce.
- Automatic Updates and Maintenance: Cloud providers handle the infrastructure’s maintenance, including software updates, security patches, and hardware management. This relieves organizations of the burden of routine maintenance tasks, allowing them to focus on core business activities.
- Innovation and Agility: Cloud providers are at the forefront of technology innovation. They regularly introduce new features and services, ensuring that users have access to the latest advancements without the need for large capital expenditures.
Disadvantages Of The Cloud:
- Data Security Concerns: Storing data off-site can raise security concerns. Organizations need to trust their cloud providers to implement robust security measures. While reputable providers invest heavily in security, it’s essential for organizations to conduct due diligence and understand their responsibilities in securing their data.
- Monthly Expenses: While cloud services can be cost-effective in the long run, monthly subscription fees can accumulate. Organizations should carefully monitor their usage to avoid unexpected costs.
- Vendor Lock-In: Moving away from a cloud provider can be challenging due to data and application dependencies. Organizations may find themselves locked into a particular provider’s ecosystem, which can limit flexibility in the future.
On-Premise Software Or Cloud - Where Is The Trend Going?
In recent years, the technology landscape has witnessed a pronounced shift towards cloud solutions, and this trend shows no signs of slowing down. Here’s a closer look at why cloud solutions have been gaining momentum and why they are likely to continue doing so:
Flexibility:
Cloud solutions offer a level of flexibility that is unmatched by traditional On-Premise alternatives. This adaptability is vital in today’s dynamic business environment, where change is constant. Here’s how cloud flexibility is making a significant impact:
- Scaling Resources: With cloud computing, businesses can easily scale their IT resources up or down to meet changing demands. Whether it’s handling increased web traffic during a marketing campaign or adding computing power for data analysis, the cloud provides instant scalability without the need for significant upfront investments.
- Remote Work Enablement: The flexibility to access cloud services from anywhere with an internet connection has become essential, especially with the rise of remote work. Cloud-based collaboration tools, document sharing, and communication platforms have become indispensable for modern organizations.
- Global Reach: Cloud solutions enable businesses to expand globally with ease. They can deploy applications and services in data centers located worldwide, ensuring low-latency access for users across different regions.
Cost Savings:
Cost-effectiveness is a driving force behind the adoption of cloud solutions. The pay-as-you-go model is particularly appealing for organizations of all sizes, from startups to large enterprises. Here’s how cloud computing helps save costs:
- Reduced Capital Expenditure: Traditional On-Premise solutions often require substantial upfront capital expenditure for hardware, software licenses, and infrastructure setup. In contrast, cloud services eliminate the need for these significant initial investments.
- Operating Expense Model: Cloud services are typically billed on a monthly or pay-as-you-go basis, which aligns expenses with actual usage. This cost model reduces the financial burden and allows organizations to allocate resources more efficiently.
- Economies of Scale: Cloud providers operate at a massive scale, which enables them to achieve cost efficiencies that individual organizations cannot match. They can invest in cutting-edge hardware and data center technologies, passing on these benefits to customers.
Innovation:
Cloud providers are known for their continuous innovation and the rapid introduction of new features and services. This innovation cycle is advantageous for businesses that want to stay competitive and leverage the latest technology trends. Here’s how cloud providers drive innovation:
- Regular Updates: Cloud services receive frequent updates and improvements, ensuring that users have access to the latest features and security enhancements without the need for manual updates.
- AI and Machine Learning: Many cloud providers integrate AI and machine learning capabilities into their services, empowering businesses to harness the power of these technologies without developing them from scratch.
- Scalable Resources: Cloud services make it easy to access and scale advanced resources such as high-performance computing clusters, data analytics tools, and machine learning platforms, enabling organizations to innovate faster.
Comparing The Two Options
- Deployment Time: On-premise solutions generally take longer to deploy, whereas cloud solutions are quick to set up.
- Maintenance: On-premise solutions require more ongoing maintenance and updates, while cloud providers handle this for you.
- Cost: Upfront costs are higher for on-premise, but long-term costs can be lower for cloud solutions.
- Scalability: Cloud solutions are more scalable, accommodating growth without major overhauls.
Are you searching for a Cloud Engineer?
On-Premise and Cloud – Both Are Possible
In many cases, a hybrid approach works best. You can combine on-premise and cloud solutions to capitalize on the strengths of both.
- Critical Data On-Premise: Keep sensitive data on-premise for enhanced security.
- Scalable Services in the Cloud: Utilize cloud services for scalability and accessibility
Why Are Backups Important?
Backups are crucial regardless of your choice:
- Data Loss Prevention: Backups ensure you can recover data in case of hardware failures or data breaches.
- Business Continuity: Having backups in place helps minimize downtime during unforeseen events.
- Compliance: Some industries require stringent backup and data retention policies for compliance.
Conclusion
In summary, the decision between On-Premise and Cloud solutions is a pivotal one that carries far-reaching implications for businesses and organizations. Each option presents distinct advantages and considerations, and the choice should align closely with your specific needs and long-term IT strategy.
Cloud solutions are often cheaper upfront due to their pay-as-you-go model, while On-Premise involves higher initial costs.
Security depends on how well each solution is implemented. Both can be secure with proper measures in place.
Yes, many businesses use a hybrid approach to leverage the benefits of both options.