What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is already being used in numerous areas, such as data security, the IoT, and artificial intelligence. Blockchain also found its place in our ranking of the most important tech trends. A blockchain is a widely distributed, publicly viewable database in which information is stored. The benefit, compared to traditional methods of storing data, is that the platform is decentralized and used by many people, so data can be transmitted in a tamper-proof way.
The German Federal Office for Information and Security describes four main goals of blockchain technology.
- Unalterable data
- Transparent and traceable transactions
- Decentralized data storage
- No intermediaries
What Are Distributed Ledger Technologies or DLTs?
DLT, contrary to what many know, is an encroachment on the blockchain. DLT (distributed ledger technologies) describe digital and decentralized ledgers of accounts. They can distribute information with a high degree of transparency and security. Distributed ledgers are, at their core, models of digital collaboration. A platform is not owned by a company, but by the users of the system.
How Does the Blockchain-Technology Work?
A blockchain is one of many ways to store data. A block contains a certain amount of information, for example, that person A has paid amount X to person B. The information is stored in a new block. When the block is “full”, a new block is added to store information. Finally, all blocks together, since they are connected by a chain, provide information about who paid whom and how much. The key advantage here is the decentralized nature of blockchain technology, as there is no need for central parties, such as a bank in finance. Once a block of information is attached to the chain, it cannot be removed or changed. This is the main reason why blockchain is so secure.
How Blockchain Works With Bitcoin
The functioning of blockchain technology can be explained with the cryptocurrency Bitcoin. A blockchain is one of the many ways to store data – in the case of Bitcoin, this information is about payments. Thus, a block in the cryptocurrency Bitcoin contains information about the payments of a wide variety of people. Bitcoin’s decentralized structure means that central parties, such as banks or other intermediaries, are bypassed.
What Are Promising Blockchain Applications?
Experts have already proclaimed the age of blockchain. In which areas do the potential of the blockchain lie? Some areas that are already benefiting from the blockchain or would not exist without it are:
- Smart-Contracts
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Cybersecurity
- Cryptocurrency
DLT technologies like blockchain are familiar to most people, but often blockchain is associated only with Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies. For many, the potential of blockchain to rethink the way we do business remains unclear.
A promising application of the blockchain can be found in Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization. Distributed leather (“distributed ledger”) allows the Ethereum platform and its users to create, manage and execute decentralized programs, such as smart contracts. One company researching this area is Bosch. Bosch is exploring the Ethereum platform with projects such as self-charging and self-paying cars at electric charging stations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain
There are many points in favor of blockchain. In particular, the higher security and the promising areas of application are reasons why the technology will gain in importance in the next few years.
Nevertheless, the topic is still quite young and just enjoying its great hype. For most, blockchain is a new and unexplored area. For this reason, there are also some criticisms to consider, which need to be solved in the future.
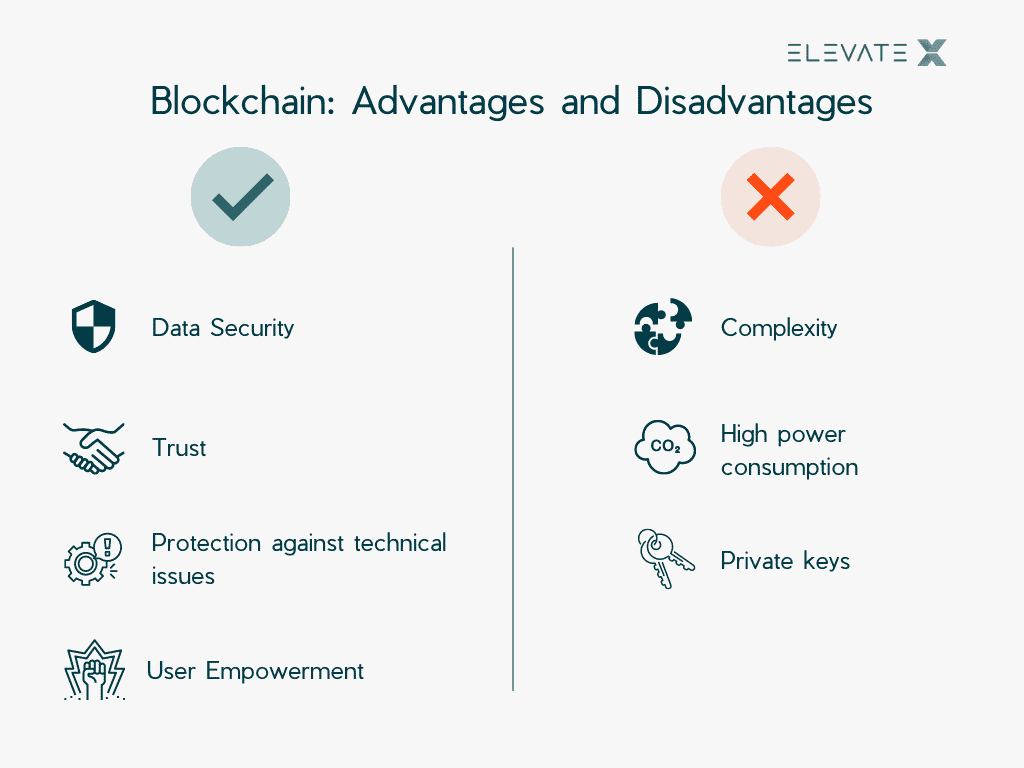
Advantages
- Security
The fact that attached information can not be changed that easily means that they are very well protected against manipulation. In addition, all actions performed can be viewed, which means that every step and every action can be monitored and also checked afterward. - Trust
In most systems where trading takes place, more than two parties are usually required. There is often an intermediary, such as a bank or credit institution. With blockchain, these intermediaries are not needed and transactions are limited to sellers and buyers only. This creates trust and additionally reduces costs for third-party providers or intermediaries. - Protection Against Technical Issues
With the blockchain, each participant stores all existing data on his or her device. For this reason, no central servers are needed. This means greater protection against data loss. If a device goes offline, it does not affect access to data, as enough other devices can provide the same information. Individual servers are more vulnerable to cyberattacks or failures. - User Empowerment
Because the blockchain is publicly visible, users have a better overview of existing data. This makes it easier for them to see what information is being stored about them and, if necessary, gives them better opportunities to defend themselves against it. At the same time, this fact ensures that companies automatically have to deal more transparently with the data of their customers or users.
Disadvantages
- Complexity
For most, blockchain is a new and under-researched area in IT. While there are many ideas and strategies to implement blockchain, it often fails due to the complexity and unavailability of experts. - High Power Consumption
To make sure that each transaction is intentional, it must run through a series of processes. Such processes also require a lot of computing power, which additionally increases energy consumption.
- Private Keys
Each part of the chain has its own address. This address can be shared. In addition, each part has its own private access key, which should not be shared. However, if this key is lost, there is no way to access the locked data. This means that large amounts of money may be lost and can not be restored.
What Is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is a contract based on specific software. This contract can contain a wide variety of information, obligations, and much more. The special feature of smart contracts is automation – if a contractual partner fulfills its obligations, payment can be made automatically and autonomously.
The programming language on which smart contracts are based is Solidity. It is now so advanced that developers can use the programming language to develop intelligent programs for various DLTs.
Smart Contracts in Daily Life
If you think about it more carefully, each of us has already encountered a smart contract, because, in principle, a beverage vending machine is a smart contract. The coin slot automatically gives us our drink, because we have fulfilled our contractual obligation to pay for our drink. Afterward, the other contractual partner, in this case, the vending machine, fulfills its obligations and gives us the purchased beverage.
What Is the Potential of Smart Contracts?
The use of smart contracts brings various advantages, including time and cost savings. Examples of the sensible use of digital smart contracts can be found in the financial sector. For example, an insurance company could pay out insurance sums after automated verification. This would eliminate the costs of verification and payment.
How Is the Blockchain Related to Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is the “engine” that uses the innovations of the Blockchain. In this context, the metaverse is also just a new dimension that includes “games, cinema, concerts, entertainment, social platforms, education, simulation-based training” and uses the innovations of Web 3.0 to fulfill its purpose. Blockchain is a key tool for transforming Web 1.0 and 2.0 into Web 3.0.
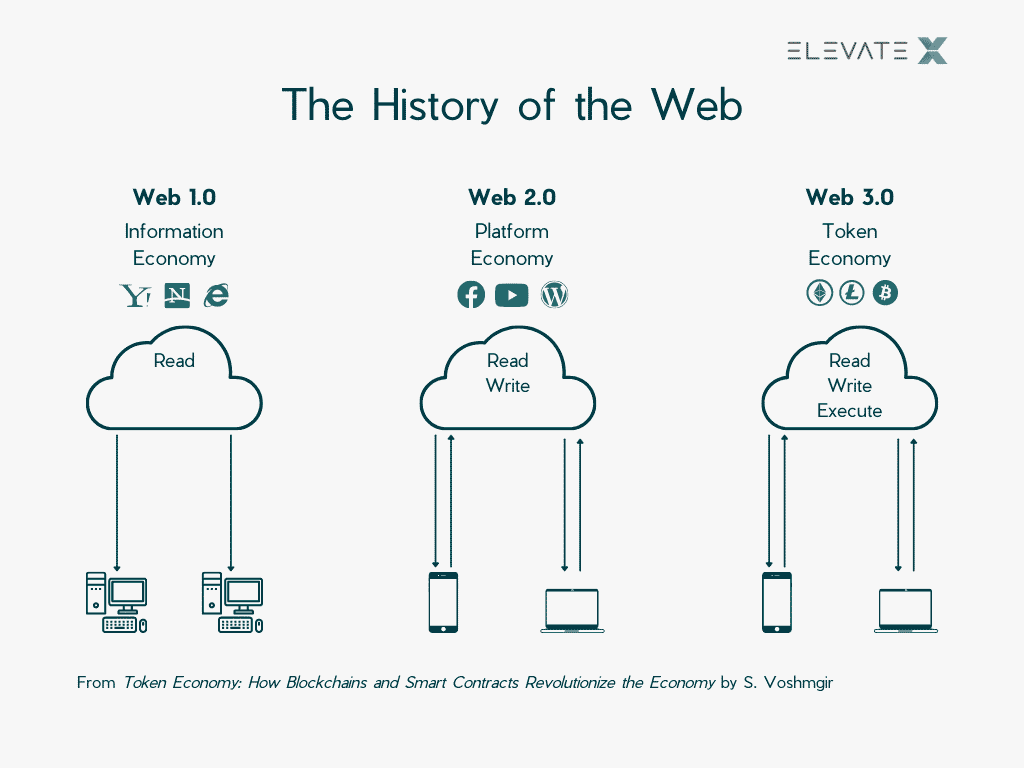
Web 1.0
Web 1.0 describes the first phase of the Internet. Companies often put image brochures online. Basically, it can be said that in Web 1.0 print was transformed into the web. Websites were usually static and interacting with them was not originally intended. For the user, this meant that he or she could only view or request information.
Web 2.0
In a smooth transition, Web 1.0 evolved into Web 2.0, at which point it was possible to interact with the Web. Completed by dynamic viewing of content and the Internet as a communication platform. Importantly, communication in Web 2.0 works both ways. Users can also create and share content for the first time in Web 2.0, keyword “user-generated content”.
Web 3.0
In Web 3.0, websites and applications should be able to process complex information through Machine Learning and Big Data. In addition, data will be connected in a decentralized manner, as with the blockchain.
Web 3.0 is based on four main functions:
- Ubiquity (availability on any smart device)
- Semantic web (decoding of emotions)
- Artificial Intelligence
- 3D-Graphics
For the user himself, not much fundamentally changes. While Web 2.0 was more of a front-end revolution, Web 3.0 is more about back-end technology. In other words, the technologies in the background, how the Internet is connected, and which technologies (blockchain) are used for this. In addition, the decentralization of information means that individual servers are no longer responsible for storing data. This means that companies like Facebook no longer have a single monopoly on user data.
Blockchain FAQ
Blockchain is a widely distributed, publicly viewable database. Blockchains are decentralized and are not located on one or more servers. Since it is difficult to change information once it has been added, the blockchain is considered particularly secure.
In simple terms, smart contracts are automated contracts. If a contracting party fulfills its obligations, payment can be made automatically and autonomously. For example in the financial sector, this would save time and money.
The blockchain describes the engine of Web 3.0. It has no direct influence on the appearance of the Internet, but regulates processes and technologies in the background, creating new opportunities. This applies especially to machine learning, AI, and Big Data.